Past Perfect Tense
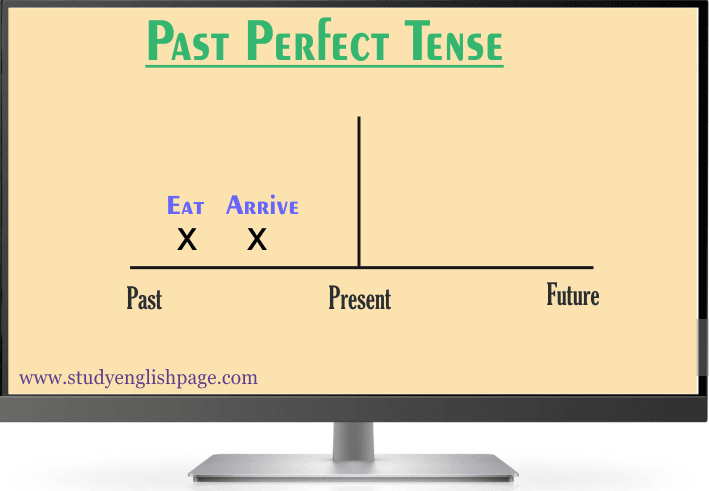
Past perfect tense shows an action which happened in the past before another action in the past.
Examples:
·
They had eaten when guests arrived at their home. (view pic)
·
I had finished my homework by the time you called me.
·
She had left for New York when I reached the airport.
Examples:
·
They had eaten when guests arrived at their home.
·
They had never seen such beautiful views
before I went there.
·
I did not have any money for shopping because I had
left my wallet at home.
·
Ali told all about Venice because he had visited the city
many times.
·
We had difficulty in searching for a hotel room because
we had not booked in advance.
Possibly, we can use specific time words or expressions with
the past perfect tense. It is usually not necessary.
Example:
·
She had visited UAE once in 2018 before she had the trip with
you in 2020.
In some cases, we use ‘after’ and ‘before’ in the past perfect to
show that one action had taken place before another. In this case past perfect
is optional. Both clauses of simple past can be used.
Examples:
·
The patient had died before the doctor came.
·
The patient died before the doctor came.
·
After he had finished his homework, he went to the karate club.
·
After he finished his homework, he went to the karate club.
Past Perfect Forms
The past perfect is formed by using had + past participle form of the verb. In questions, we use the auxiliary ‘had’ at the beginning of the sentence. Negatives are made with not.
Affirmative:
·
Subject + had + verb in the past participle form + . . . . .
.
·
He had gotten engaged before he moved to New York.
·
Students understood the movie well because they had
read the novel book.
· Hassan had never been to a concert before last night.
Negative:
Subject + had + not + verb in the past participle form + . .
. . . . .
·
He had not gotten engaged before he moved to New York.
·
I had not eaten dinner when he called.
· Students had difficulties understanding the movie because they had not read the novel book.
Interrogative:
Had + subject + verb in the past participle form + . . . . .
. .
·
Had he gotten engaged before he moved to New York?
·
Had Ali ever studied Arabic before he moved
to Iraq?
· Had you ever visited the U.S. before your trip in 2006?
Negative and Interrogative:
Had + not + subject + verb in the past participle form + . .
. . . . .
·
Had not he got engaged before he moved to New
York?
·
Hadn’t Ali ever studied Thai before he moved
to Thailand?
·
Hadn’t you ever visited the U.S. before your trip
in 2006?
Had + subject + not + verb in the past participle form + . .
. . . . .
·
Had he not got engaged before he moved to New
York?
·
Had Muh not studied Thai before he moved to
Thailand?
·
Had you not visited the U.S. before your trip in
2006?
Contract forms or short forms
|
I had |
I’d |
We had |
We’d |
|
You had |
You’d |
He had |
He’d |
|
She had |
She’d |
It had |
It’d |
|
They had |
They’d |
Had not |
Hadn’t |
·
I’d completed my homework by the time you got home.
·
We’d reached the hospital when they came.
·
You’d submitted your assignment by the time I submitted it.
·
He’d controlled the students before they started the
program.
·
She’d prepared the meal by the time we reached there.
·
It’d blasted when you called me.
·
They’d finished the meeting when I reached because I was
late.
·
He hadn’t studied English before he moved to New York.
Yes/No Questions and short Answers
A question that is answered by Yes or No is called a Yes/No
Question.
A short answer means to use just subject and auxiliary after
yes or no to give an answer. A comma is used after Yes or No.
Ex:
·
Had you studied English when you went to New York?
Yes, I had.
·
Had he left the job when he got the appointment for the new job?
No, he had not.
Information Questions (wh questions) and Answers
A question that is asked to interrogate or get information
is called an information question.
Ex:
·
What had she studied when she moved to Germany?
She had studied computer
programming when she moved to Germany.
·
Where had they gone by the time our father got home?
They had gone on a picnic by
the time your father got home.
·
Why had not she done her homework before she went to bed?
Because she had had important
work before she went to bed.
·
Who had eaten by the time we started to eat?
Tom had eaten by the time we
started to eat.
·
Whose report had the police cleared by the time they were
arrested?
Police had cleared Ali’s report
by the time they were arrested.
·
Which book had you bought before I told you?
I had bought English Grammar
Book before you told me.
·
How had it rained when we came?
It had rained cats and dogs
when you came.