Present Continuous Tense
An action which is happening right now is called Present Progressive Tense. An action which is going on at the time of speech.
Ex:
- I am writing a letter.
- He is doing his homework.
- They are reading a newspaper.
Graphical
Interpretation:
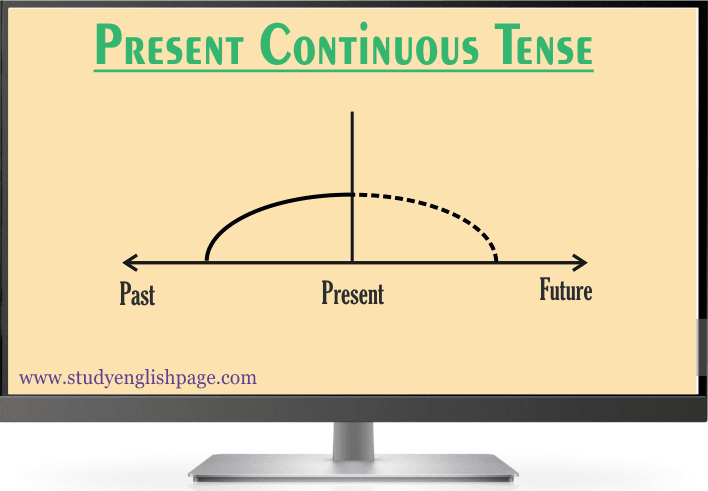
An action which commenced in the past, is occurring right now and will probably occur in the future. Examples:
- They are reading their books.
- They are watching television.
- She is becoming tired.
- I am doing my homework.
Present
Continuous Forms
Affirmative:
Subject + am/is/are + verb + ing + object…..
- You are watching TV.
- He is knocking at the door.
- I am doing my homework.
- They are attending the meeting.
Negative:
Subject + am/is/are + not + verb + ing + object….
- You are not watching TV.
- She is not peeling potatoes.
- I am not doing my homework now.
- They are not attending the meeting. They are discussing something else.
Interrogative:
Am/is/are +subject + verb + ing + object …..
- Are you watching TV?
- Is he leading a humiliating life?
- Am I going somewhere else?
- Are they attending the meeting?
Negative and Interrogative:
Am/is/are + not + subject + verb + ing +object …...
- Aren't you watching TV?
- Isn't he leading a humiliating life?
- Aren't I going somewhere else?
- Aren't they attending the meeting?
Am/is/are + subject + not + verb + ing + object…..
- Are you not watching TV?
- Is he not leading humiliating life?
- Am I not going somewhere else?
- Are they not attending the meeting?
Yes/No Questions and short Answers
A question which is answered by Yes or No is called a Yes/No
Question.
A short answer means to use just subject and auxiliary after
yes or no to answer. A comma is used after Yes or No.
Ex:
- Are you writing?
Yes, I am.
- Is it raining?
No, it is not.
- Are they asking about me?
Yes, they are.
Information Questions (wh questions) and Answers
A question that is asked to interrogate or get information
is called an information question.
Ex:
- What are you doing?
I am cleaning the kitchen.
- Where is she studying?
She is studying in the garden.
- Why are they not answering?
Because they are not listening.
- Who is talking?
Ali is talking to his mother.
- Whose car is coming?
Ali’s car is coming.
- Which book is she studying?
She is studying English Grammar Book.
- How is she listening?
She is listening attentively.
Contract forms or short forms
|
Short
form |
Short
form |
||
|
He is |
He’s |
He is
not |
He
isn’t |
|
She
is |
She’s |
She
is not |
She
isn’t |
|
It is |
It’s |
It is
not |
It
isn’t |
|
They
are |
They’re |
They
are not |
They
aren’t |
|
I am |
I’m |
I am
not |
I
ain’t |
|
We
are |
We’re |
We
are not |
We
aren’t |
|
You
are |
You’re |
You
are not |
You
aren’t |
|
Ali
is |
Ali’s |
Ali
is not |
Ali
isn’t |
- She’s becoming tired.
- I’m doing my homework.
- You’re watching TV.
- You aren’t watching TV.
- She isn’t peeling potatoes.
- I ain’t doing my homework now.
- They aren’t attending the meeting. They are discussing something else.
- Aren’t you watching TV?
- Isn’t he leading a humiliating life?
- Ain’t I going somewhere else?
- Aren’t they attending the meeting?
How to get the Ing-Form (Present Participle From) of the verb?
1) The general rule when changing a verb into its -ING form
is just to add -ING to the end of the verb.
|
Feel |
feeling |
|
Go |
going |
|
Work |
working |
|
Sleep |
sleeping |
- She isn't feeling very well.
- He is working on a new project.
- The children are sleeping so be quiet.
2). If the verb ends in an 'E', we remove the E and add ING.
|
Live |
living |
|
Have |
having |
|
Make |
making |
|
Take |
taking |
- We are making a chocolate cake.
- He is taking his time to get ready.
- We are living in the same room.
3). If the verb ends in a consonant + vowel + consonant, we
double the final consonant and add ING.
|
Stop |
stopping |
|
Sit |
sitting |
|
Plan |
planning |
|
Get |
getting |
|
Swim |
swimming |
- The policeman is stopping the traffic.
- We are planning a party for our high school teachers.
- I think I am getting a cold.
4). If a two-syllable verb ends in a consonant + vowel +
consonant and there is stress on the first syllable, we do not double
the final consonant.
|
Happen |
happening |
|
Enter |
entering |
|
Offer |
offering |
|
Suffer |
suffering |
- What is happening?
- They are offering a discount.
- Many people are suffering from Coronavirus in the world.
5). But, we do not double the final consonant when the verb
ends in W, X, or Y or when the final syllable is not stressed.
|
Fix |
fixing |
|
Enjoy |
enjoying |
|
Snow |
snowing |
- He is fixing his bike.
- We are enjoying this great weather.
- It's snowing outside.
6). If the verb ends in IE we change it to Y and add ING.
|
Lie |
lying |
|
Die |
dying |
|
Tie |
tying |
- I know you are lying to me!
- You should water your plants twice a day because they are dying.
- The little boy is tying his shoelaces.
7). If the verb ends in consonant + vowel + L, we normally
double the final L and add ING.
Note: According to American English, we do not
double the L when the accent is on the first syllable.
|
ING form (UK) |
ING form (US |
|
|
Travel |
travelling |
traveling |
|
Marvel |
marvelling |
Marveling |
- I am travelling.
- He is marvelling at her beauty.
8). When a verb ends in a stressed vowel + R, we double the
final R and add ING.
|
Refer |
referring |
|
Defer |
deferring |
- Are you referring me to Dr. Asim?
- I am deferring my class.
9). When a verb ends in an unstressed vowel + R, we
do not double the final R and add ING.
|
Offer |
offering |
|
Suffer |
suffering |
|
Whisper |
whispering |
- I am offering you a special deal.
- He is now suffering from a fever.
- What is he whispering in her ear?




0 Comments